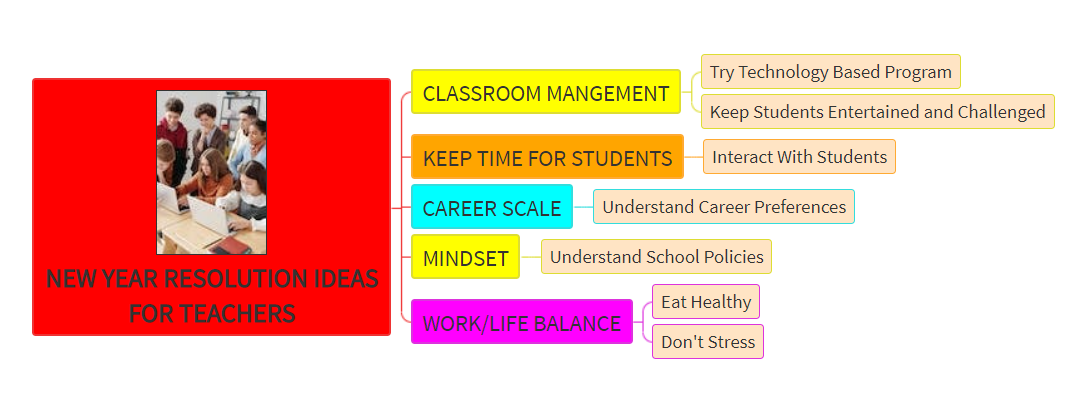
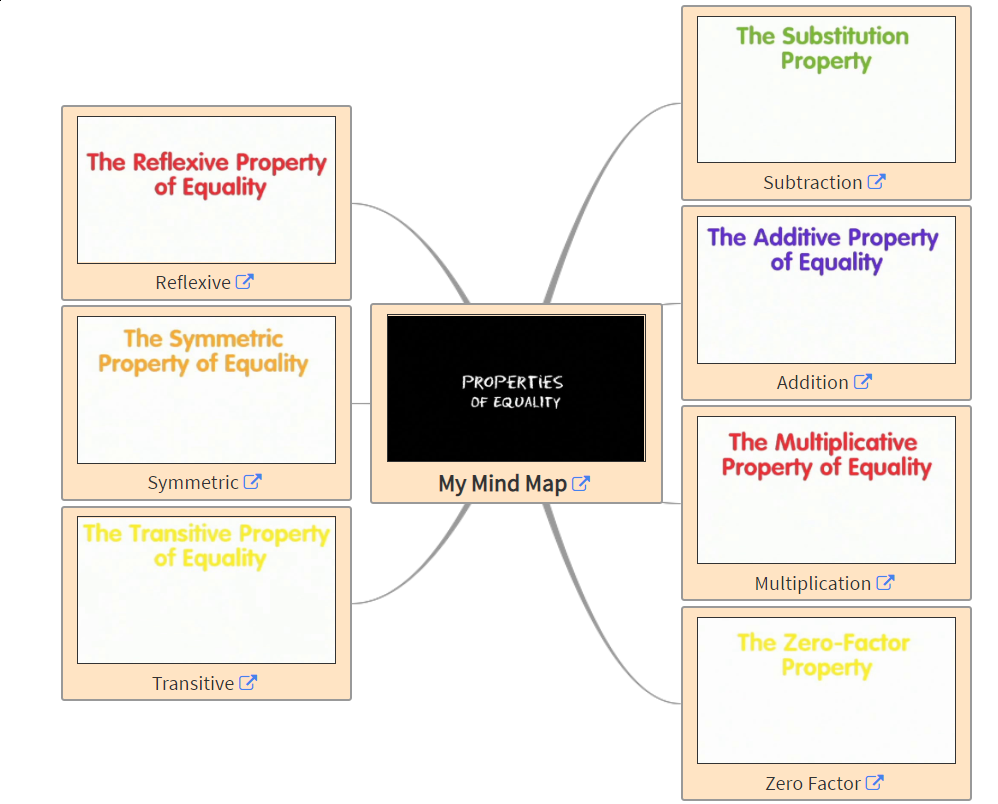
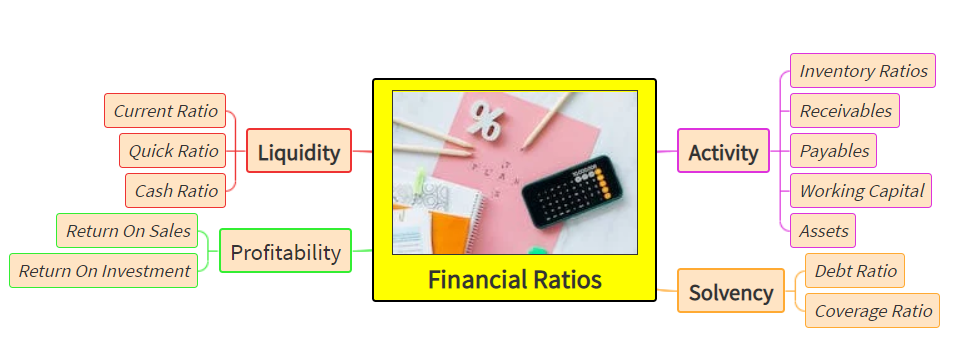
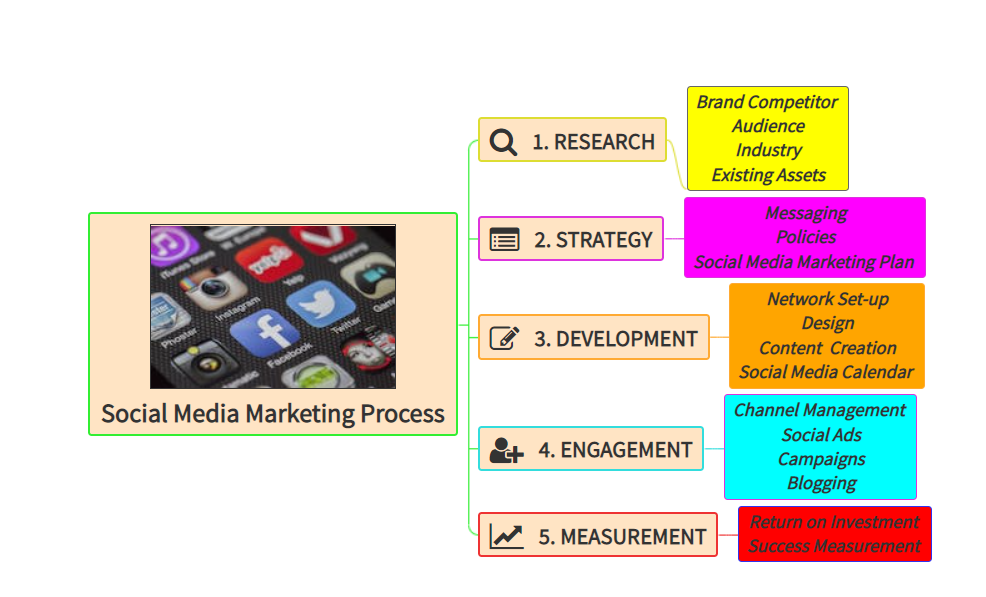
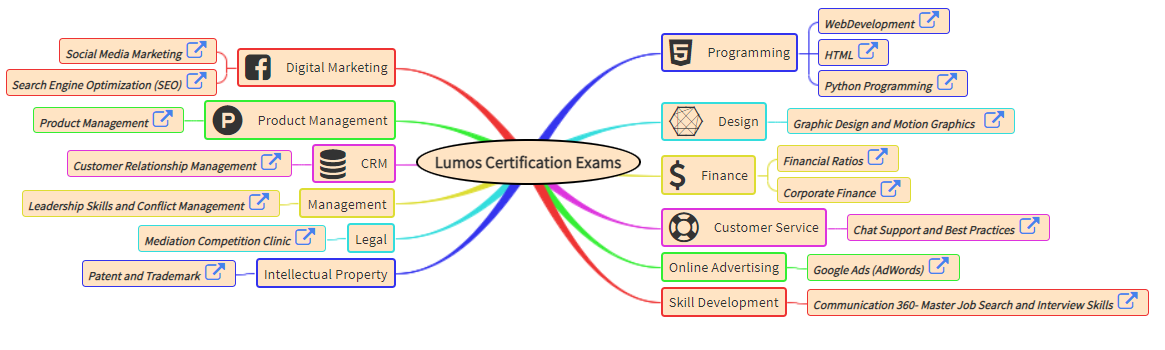
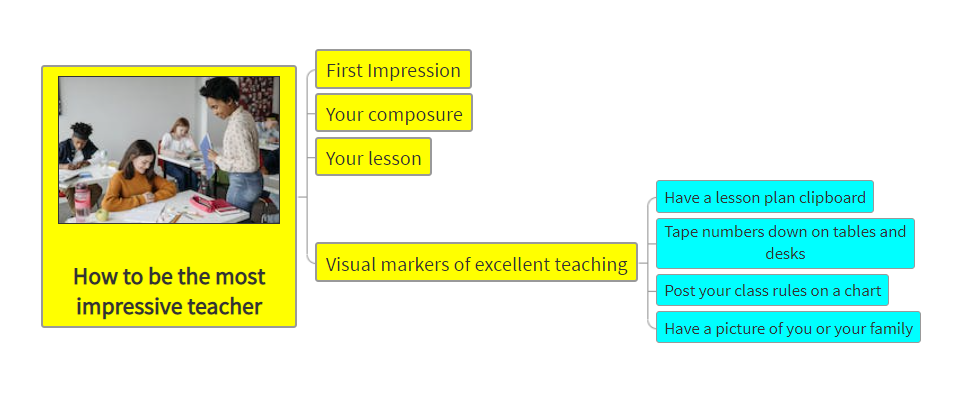
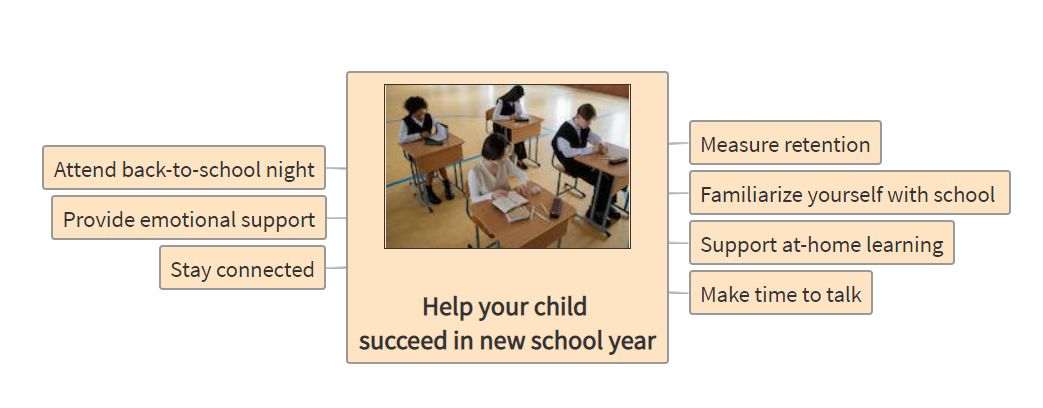
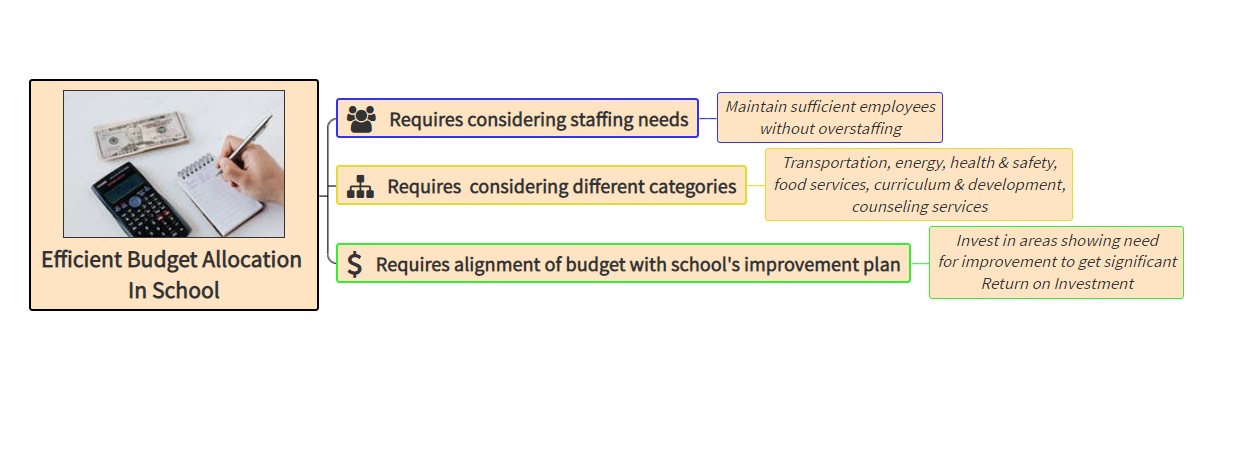
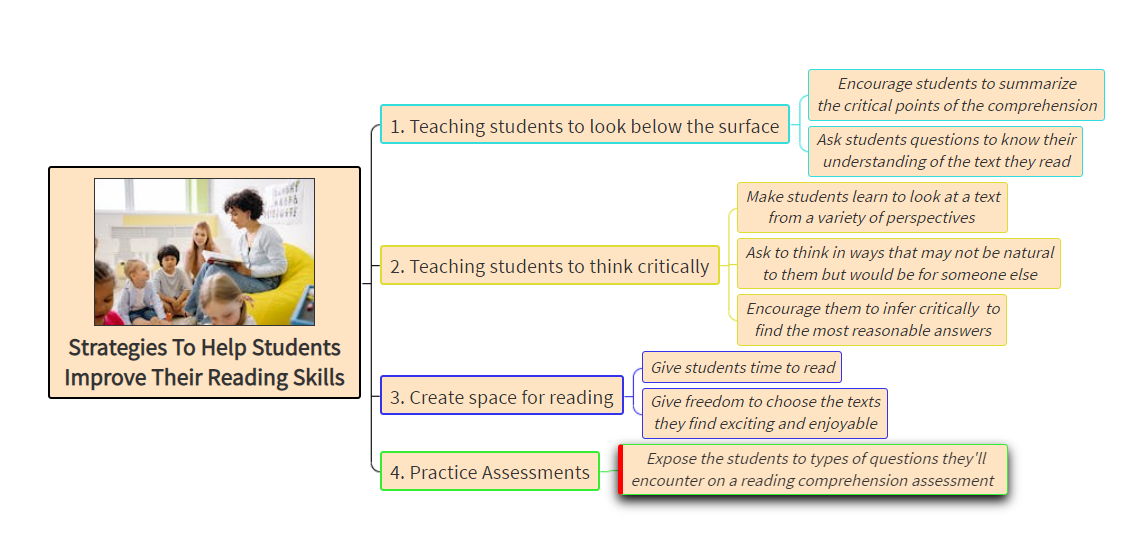
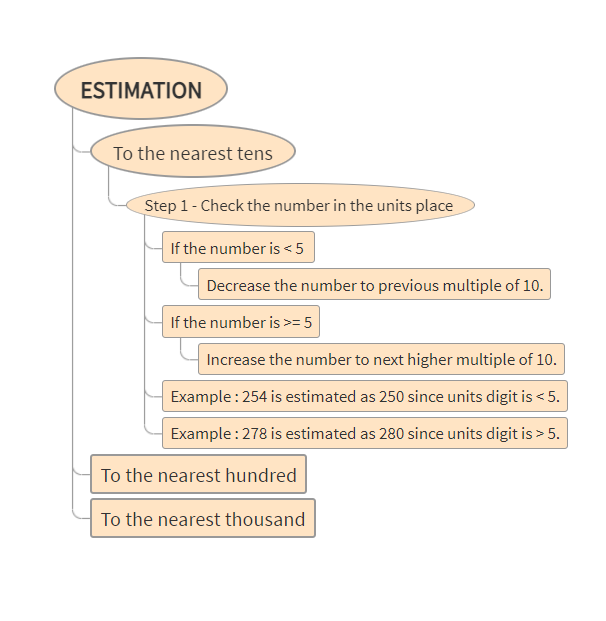
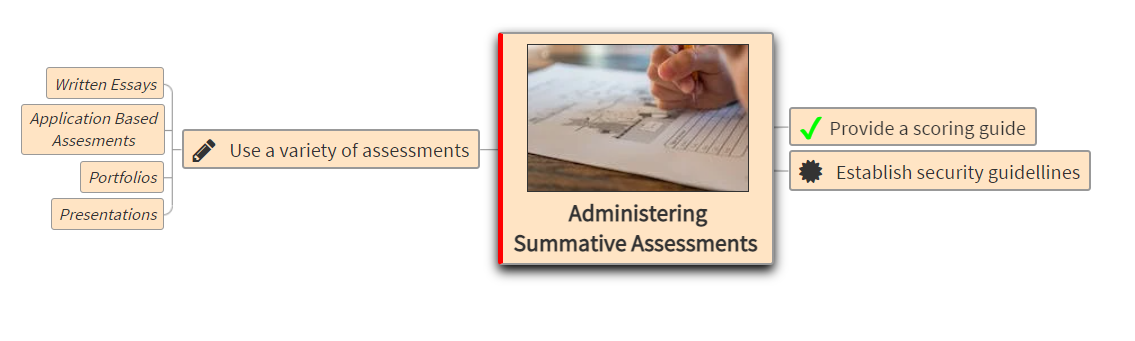
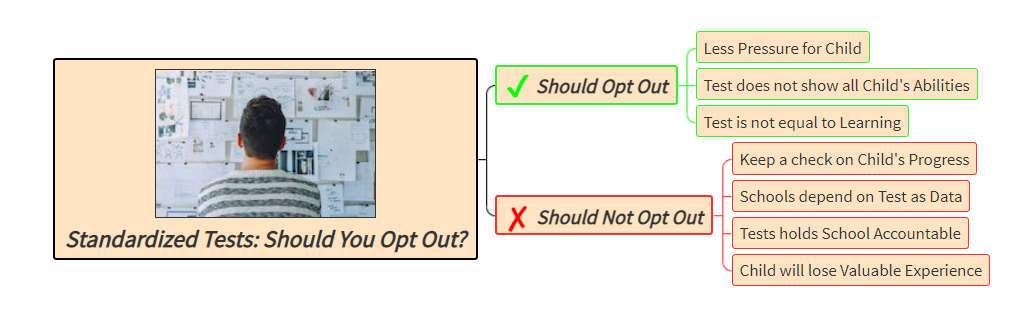
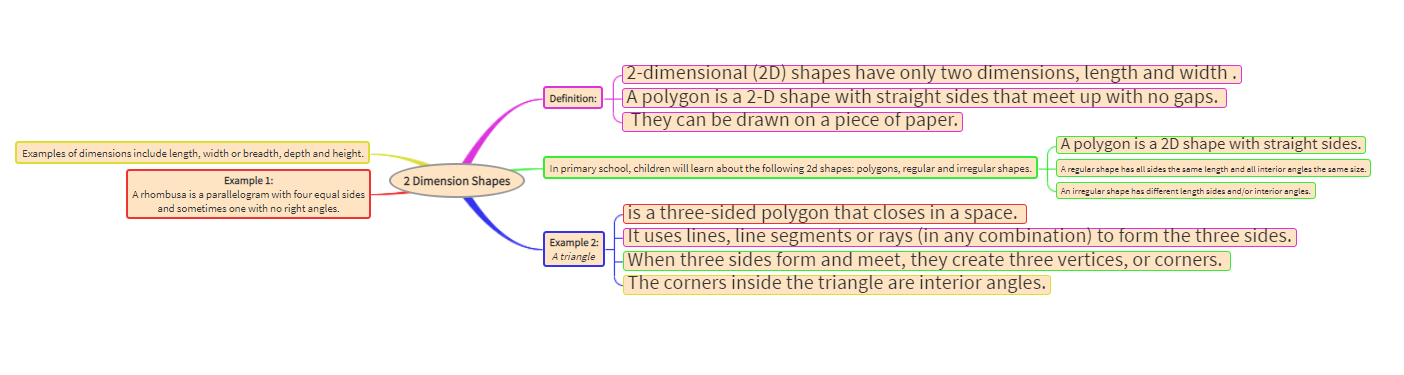
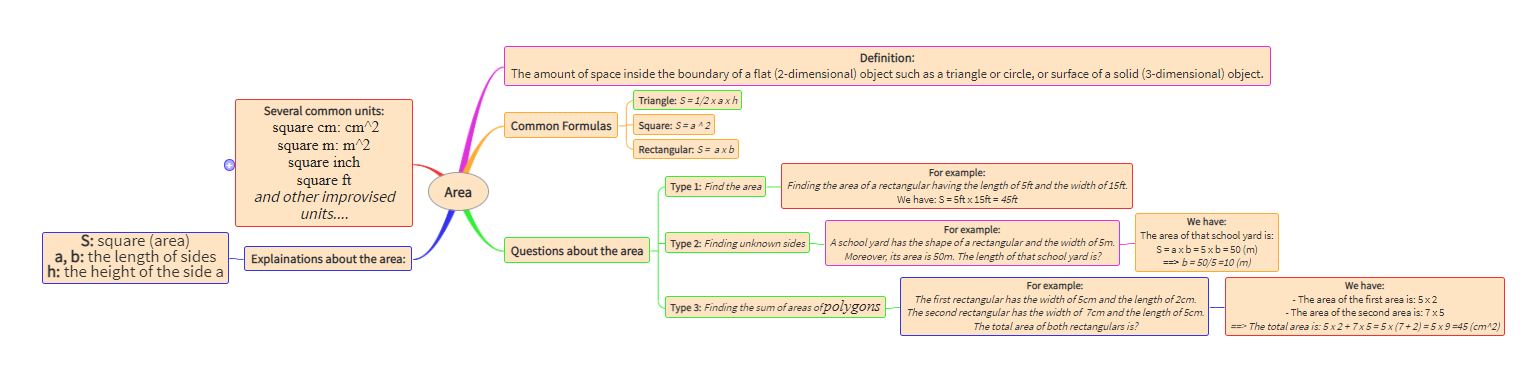
Description: Parts of the eye and its functions
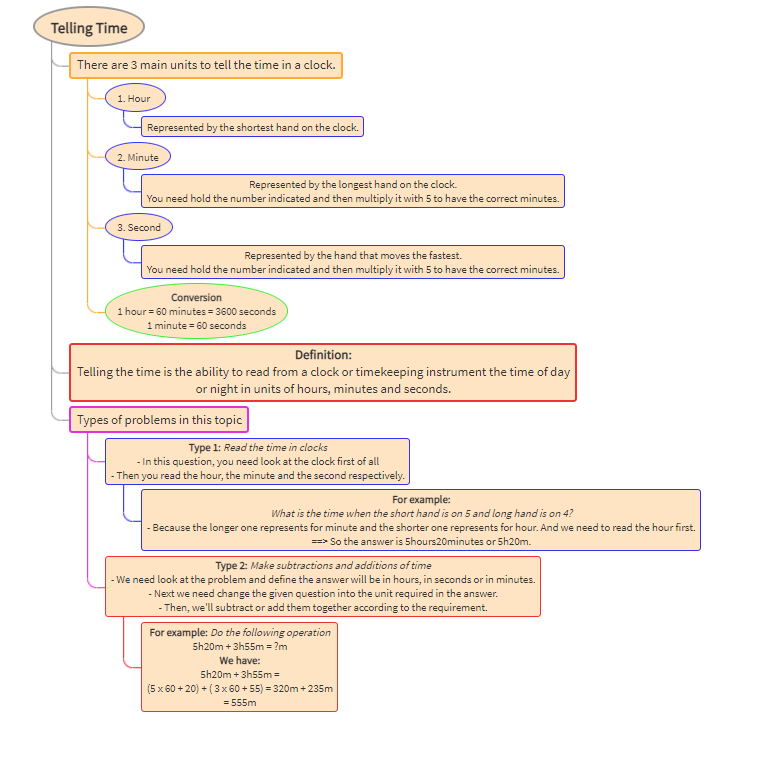
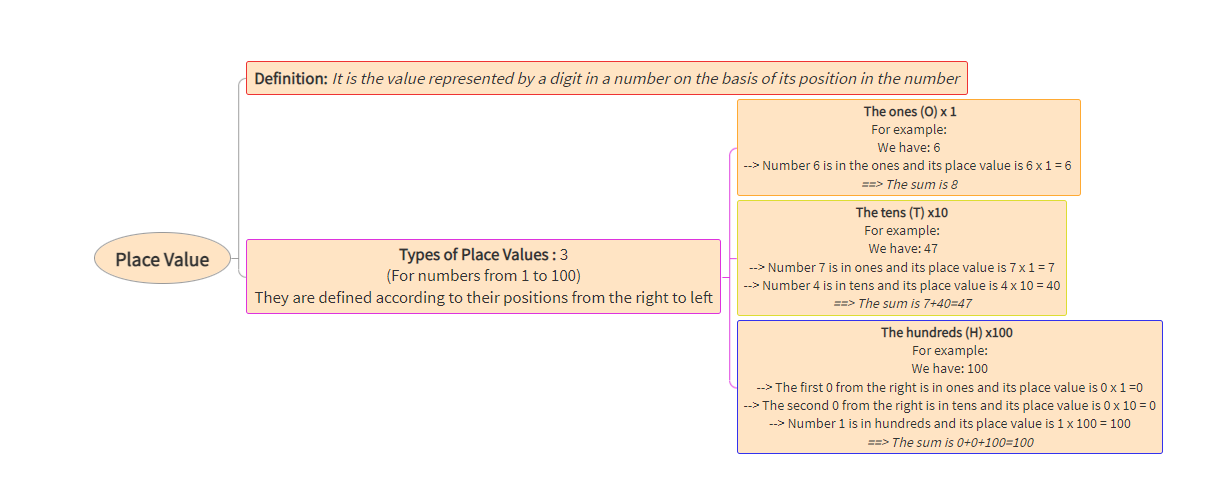
Structure of the Eye and Retina
Ganglion cells
Receives messages from bipolar cells
(rods and cones) and the ganglion cells
Signals join together (close to the center of the eye)
and travel to the brain.- Blind spot
The ganglion cells form the optic nerve.
The point in which it leaves the eye is a blind spot
as there are no receptors.
- Blind spot
Cones
Less active in dim light and are
essential in color vision.
Abundant in and near the fovea.- Red
Longwave
700nm - Green
Mediumwave
500nm - Blue
Shortwave
350nm
- Red
Fovea
The pit at the back of the eye
that is specialized for acute,
detailed vision.- Rods
Respond to faint light and are
not useful in daylight.
Bright light bleaches them.
Abundant in the periphery
of the human retina. - blood vessels are almost absent
and ganglion
cells ensure unimpeded vision
- Rods
Retina
Where the light is projected
at the rear surface of the eye.
Is lined with visual receptors.- Light always strikes
the opposing side
- Light always strikes
Pupil
Center of the iris (colored area)
in which light enters through
and opening in the center and is
projected on the back of the eye.- Lens
Focuses the pupil, is adjustable - Cornea
Focus the pupil,
is not adjustable
- Lens