Parts of Speech Made Easy with AI-powered Mind Maps
Imagine if teaching parts of speech could be as fun and easy as connecting the dots in a colorful picture. Well, buckle up because we’re about to dive into a super cool tool that’s going to make explaining grammar a breeze – AI-powered mind maps!
Say goodbye to the days of paper and pen grammar lessons, and let’s explore a whole new world of teaching where learning parts of speech becomes an exciting adventure for both you and your students. Welcome to the future of language education!
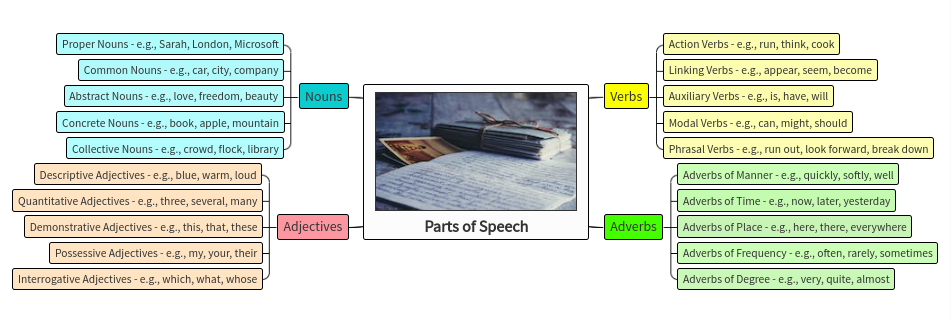
Table of contents
How Mind Maps Can Help With Learning Parts of Speech
Creating a Mind Map on Parts of Speech: Step-by-Step Guide With Lumos StepUp
How Mind Maps Can Help With Learning Parts of Speech
Mind maps serve as invaluable tools for learning parts of speech, offering a structured and visual approach to understanding the intricacies of language. Here’s how mind maps can facilitate the learning process:
- Visual Representation: Mind maps provide a visually appealing representation of parts of speech, making complex concepts easier to comprehend. Each part of speech can be visually organized, allowing learners to see the relationships between different types of words.
- Simplification: By breaking down parts of speech into bite-sized chunks, mind maps simplify the learning process. Students can focus on one category of words at a time, gradually building their understanding before moving on to more advanced topics.
- Active Engagement: Mind maps encourage active engagement with the material, as students actively participate in creating and interacting with the visual representations. This hands-on approach fosters deeper comprehension and retention of parts of speech.
- Personalized Learning: Mind maps can be customized to suit individual learning styles and preferences. Students can add their own examples, mnemonic devices, or color-coded annotations to tailor the mind maps to their needs.
- Creative Exploration: Mind maps encourage creative exploration of parts of speech, allowing students to make connections between different types of words and understand how they function within sentences. This creativity promotes a deeper understanding of language structure.
Creating a Mind Map on Parts of Speech: Step-by-Step Guide With Lumos StepUp
Step 1: Access Lumos StepUp Mind Maps
Log in to your teacher portal Lumos StepUp account and select “My Mind Maps” from the dashboard.
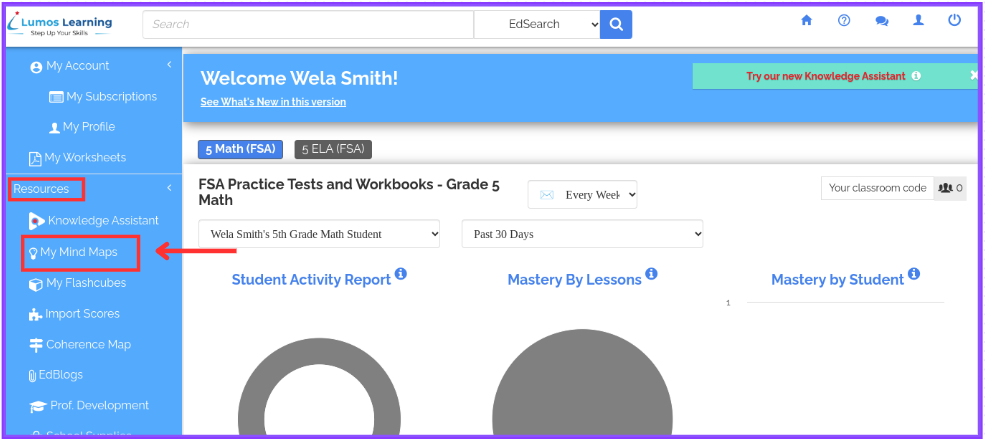
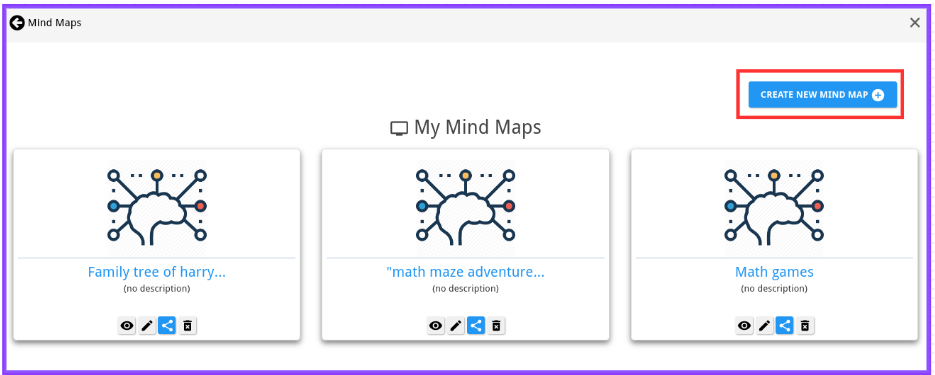
Step 2: Create a New Mind Map
Click on “Create New Mind Map” to initiate the mind map creation process.
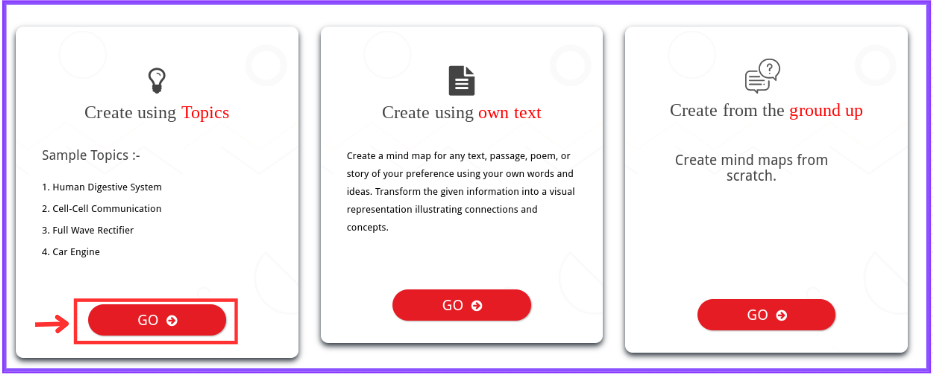
Step 3: Autogenerate Mind Map Using Topics
Select “Create using Topics” to utilize the autogeneration AI feature. Click on “GO” under “Create using Topic.”
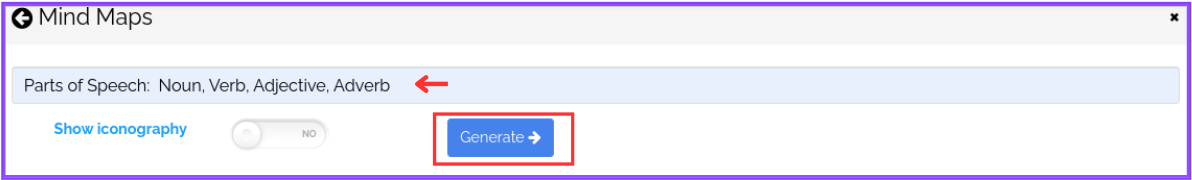
Step 4: Enter “Parts of Speech: Noun, Verb, Adjective, Adverb” as the Topic
Type or paste “Parts of Speech: Noun, Verb, Adjective, Adverb” in the provided text space and click on “Generate.” The system will take 2-3 minutes to autogenerate the mind map based on the chosen topic.
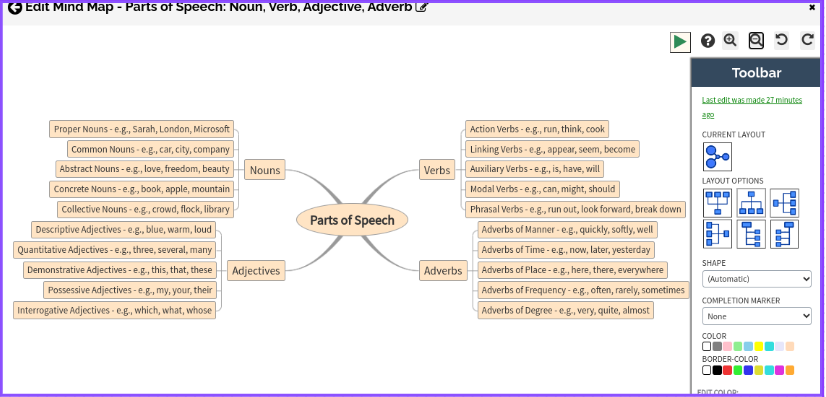
Step 5: Edit and Customize
Once autogeneration is complete, you’ll have an illustrated mind map of Parts of Speech. Feel free to edit, and add colors, images, and icons to tailor the mind map to your preferences
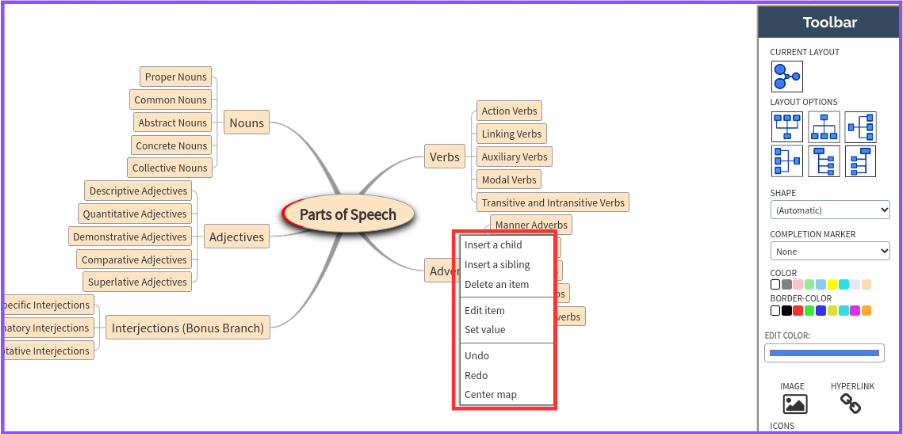
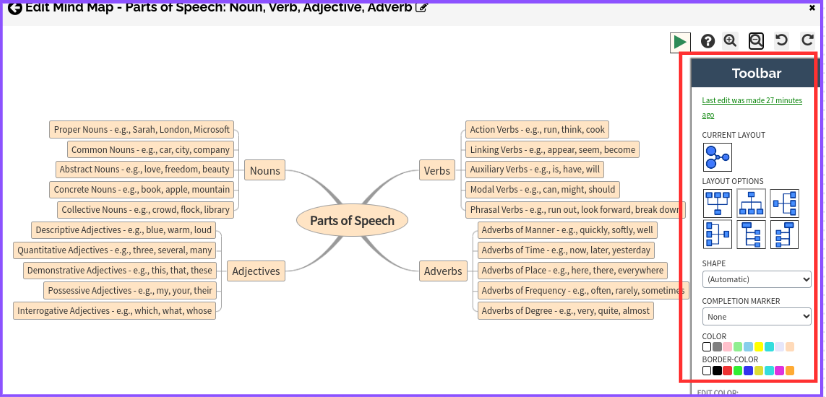
How to Edit Your AI-generated Mind Map
- Right-click on any of the box items to see available options, such as adding a text box, sub-items, deleting items, editing items, setting values, and more.
- Use the “Toolbar” on the right side of your screen to change the mind map layout, and shape, add/remove completion markers, add color, insert images, hyperlink text, and add icons for a visually appealing mind map.
Encourage Students to Try AI-Powered Mind Maps
Once you have created your AI-generated mind map, share it with your students to view/edit the mind map and encourage them to create new mind maps on their own. You can do that as a classroom activity or give it to them as a homework assignment.
How to Share Your Mind Maps
Step 1: Click on the “Share” icon under your created mind map present on the “My Mind Maps” screen.
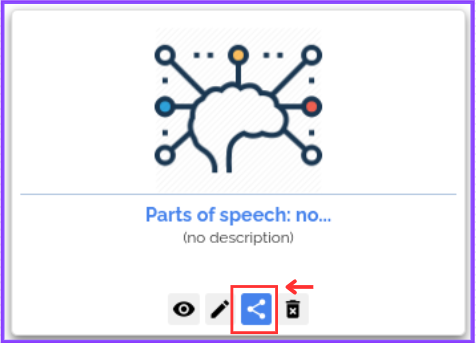
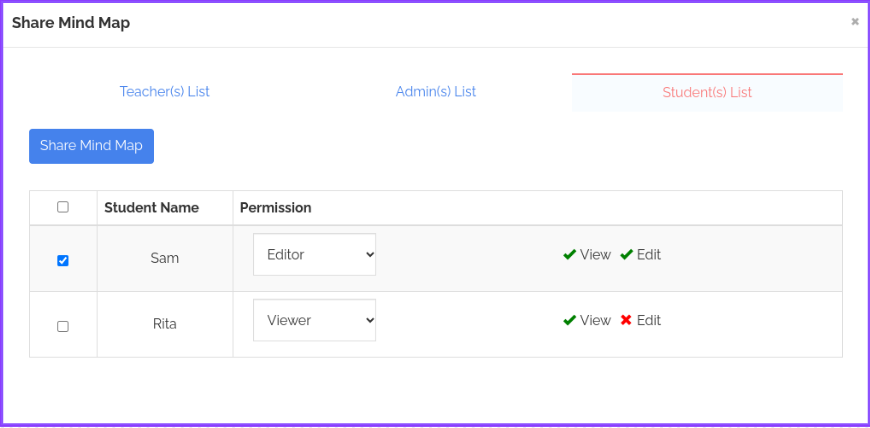
Step 2: Select the Student(s) list from the available options, then select the student(s) you want to share your mind map with and give them “View” or “Edit” permission access.
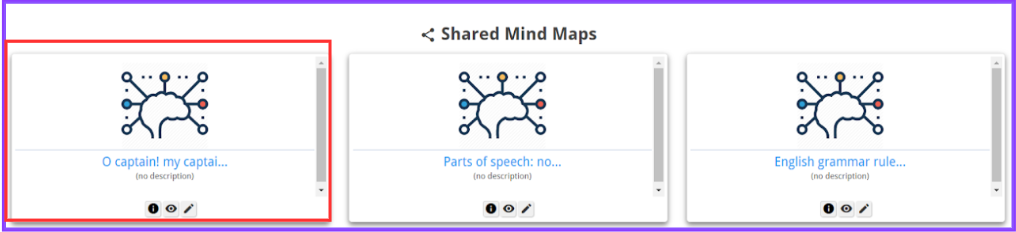
Step 3: The selected student(s) will then be able to view/edit the mind map based on the given permissions from their student accounts under the “Shared Mind Maps” section.
Using Parts of Speech Mind Maps in Class
Incorporating parts of speech mind maps into classroom instruction can revolutionize the way students engage with grammar concepts. Here’s how teachers can effectively utilize parts of speech mind maps in their lessons:
- Introduction: Start by introducing the concept of mind mapping and its relevance to understanding parts of speech. Explain how mind maps visually represent different types of words and their relationships within sentences.
- Exploration: Guide students through the exploration of various parts of speech using mind maps. Break down each category – nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections – and discuss their definitions, functions, and examples.
- Hands-on Creation: Encourage students to create their own parts of speech mind maps. Provide them with templates or guidelines for organizing the information and let them add their own examples and annotations. This hands-on activity promotes active learning and reinforces comprehension.
- Collaboration: Foster peer collaboration by having students share and discuss their mind maps with one another. Encourage them to compare their interpretations, identify similarities and differences, and ask questions to deepen their understanding of parts of speech.
- Application: Use parts of speech mind maps as teaching aids during grammar exercises and writing activities. Refer to the mind maps when analyzing sentences, identifying parts of speech, and constructing grammatically correct sentences. This practical application reinforces the concepts learned and helps students see the relevance of grammar in everyday communication.
- Assessment: Assess students’ understanding of parts of speech through quizzes, assignments, or presentations based on their mind maps. Evaluate their ability to accurately categorize words, identify examples, and explain the functions of different parts of speech. Provide constructive feedback to guide their further learning.
Conclusion
Incorporating parts of speech mind maps into classroom instruction offers a dynamic and engaging approach to teaching grammar. By visually representing the various types of words and their functions within sentences, mind maps provide students with a clear and structured framework for understanding parts of speech.
By embracing this innovative teaching tool, educators can cultivate a deeper appreciation for grammar among their students and equip them with the skills they need to communicate effectively. Whether preparing for standardized tests, refining writing skills, or simply exploring the nuances of language, parts of speech mind maps offer a valuable resource for language learners of all levels.
