Improving Math Learning with Mind Maps
Welcome to the world of modern education, where innovative tools are revolutionizing the way we teach math. Mind maps are one such tool, offering a dynamic approach to learning that improves how students understand and remember mathematical concepts. Join us as we explore how mind maps can transform the math classroom, making learning more engaging and effective for your students.
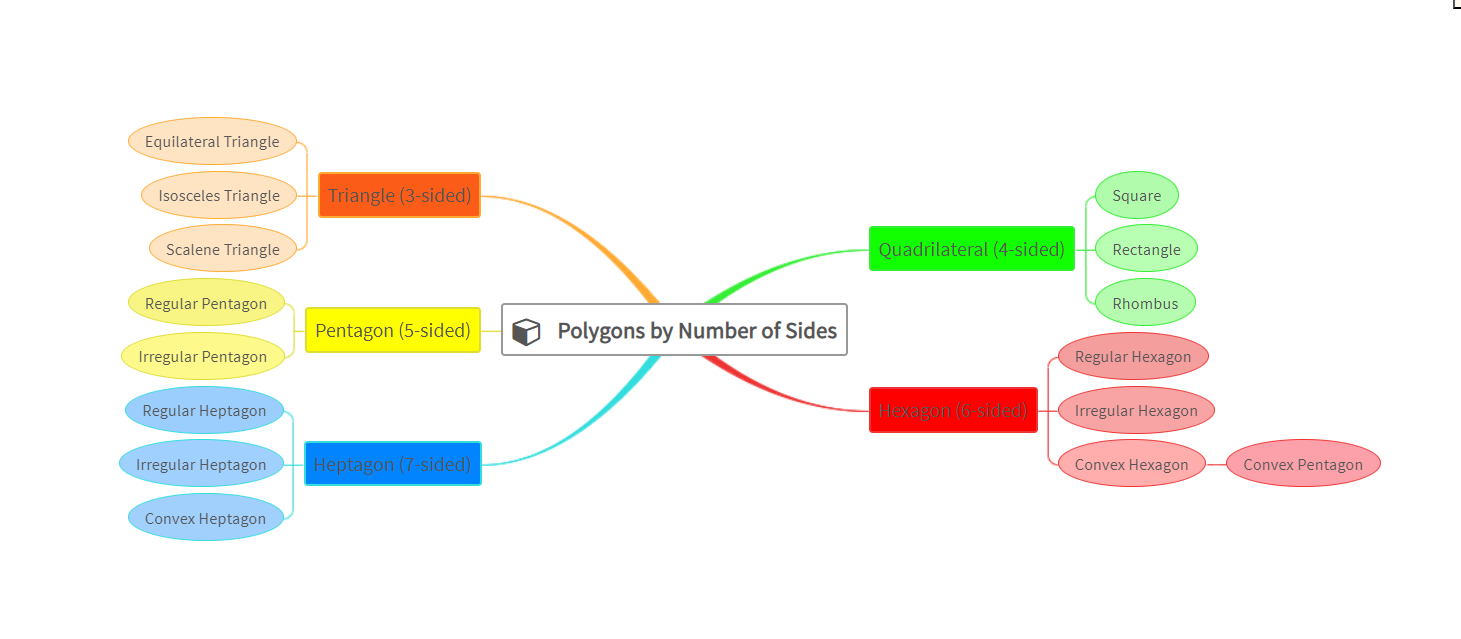
Table of contents
The Power of Mind Maps in Math Education
Creating a Mind Map on Polygons: Step-by-Step Guide With Lumos StepUp
The Power of Mind Maps in Math Education

Image by archjoe on Freepik
Mind maps transcend traditional teaching methods, providing a dynamic platform for students to explore mathematical concepts from multiple perspectives. These colorful diagrams stimulate both hemispheres of the brain, fostering connections between ideas and promoting creative problem-solving.
Here’s how mind maps can benefit our students in the math classroom:
Enhanced Comprehension
Mind maps serve as visual roadmaps for understanding complex mathematical concepts, offering a bird’s-eye view of the terrain while zooming in on specific details. By organizing information hierarchically around central themes, such as mathematical topics or problems, mind maps help students grasp abstract concepts with ease.
Improved Memory Retention
The visual nature of mind maps transforms them into powerful memory aids. By creating spatial relationships between concepts and leveraging visual cues like colors, shapes, and images, students can encode mathematical information more deeply into their long-term memory. This facilitates better recall and retention of key math concepts over time.
Promotes Critical Thinking
Through the creation and manipulation of mind maps, students engage in active analysis of mathematical ideas, identifying patterns, and making logical connections. This process fosters a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts and cultivates higher-order thinking skills essential for problem-solving.
Facilitates Collaboration
Mind maps encourage collaborative learning in the math classroom, fostering peer-to-peer communication and knowledge-sharing. By collaboratively creating and discussing mind maps, students can exchange ideas, share their understanding of math concepts, and collaborate on problem-solving activities.
Now, let’s delve into a practical example of how we can leverage the power of mind maps in the math classroom with the topic “Polygons by Number of Sides.”
Creating a Mind Map on Polygons: Step-by-Step Guide With Lumos StepUp
Imagine guiding your students through a lesson on polygons and their properties using an interactive mind map.Let’s dive into the process of creating this mind map using the AI capabilities within your Lumos StepUp teacher account.
Step 1: On your teacher dashboard, scroll down and navigate to “Resources” on the left side of your screen and select “My Mind Maps” from the available options.
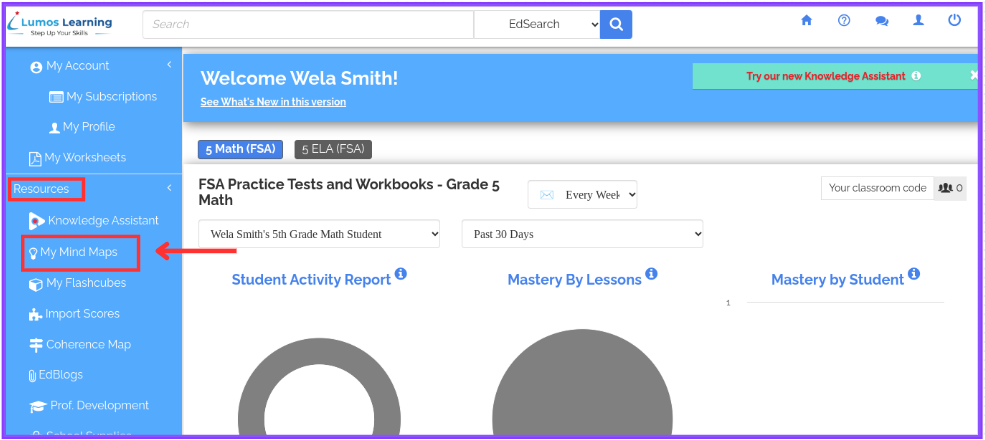
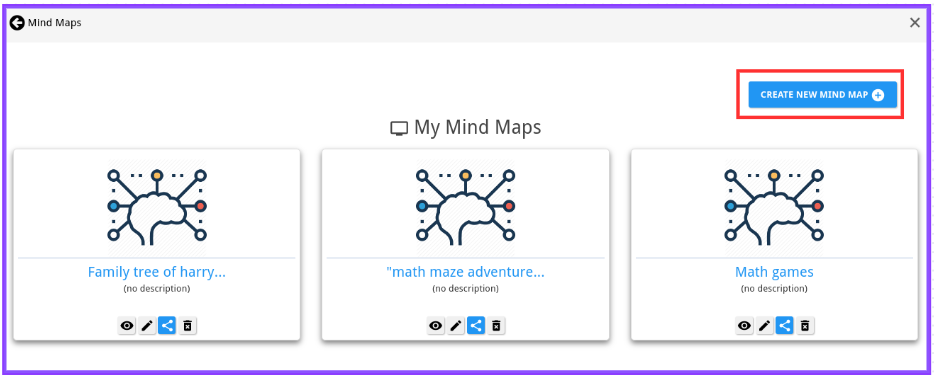
Step 2: Click on “Create New Mind Map” to start creating your mind map.
Step 3: Choose “Create using Topics” to utilize the AI autogeneration feature.
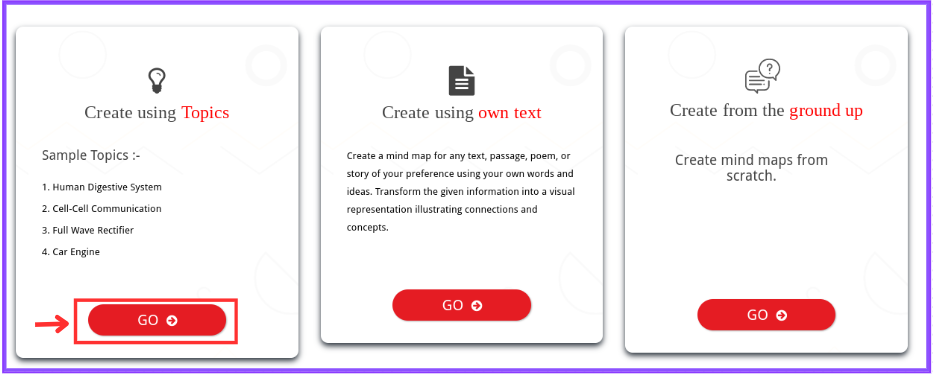
Step 4: In the text space provided, enter the topic “Polygons by Number of Sides” and click on “Generate.”
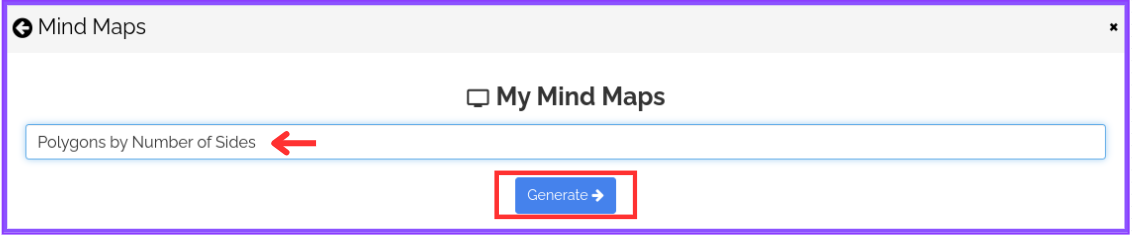
Step 5: Once autogeneration is complete, you’ll have an illustrated mind map on Polygons by Number of Sides. Feel free to edit, and add colors, images, and icons to tailor the mind map to your preferences.
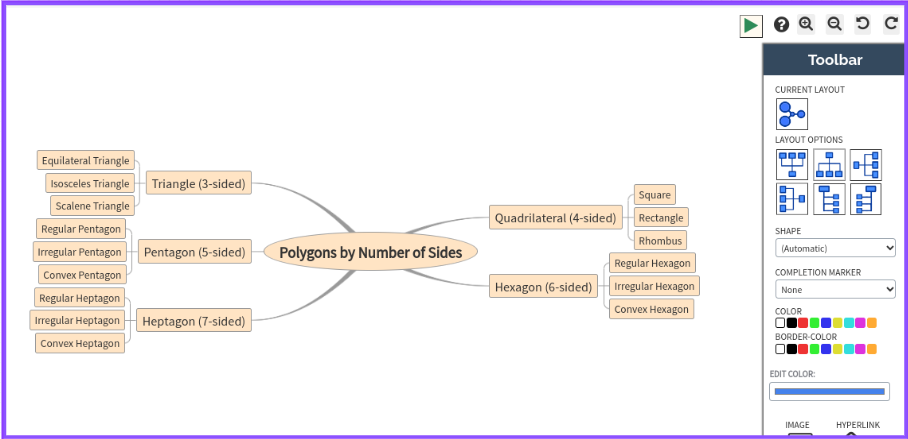
How to Edit Your AI-generated Mind Map
- Right-click on any of the box items to see available options, such as adding a text box, sub-items, deleting items, editing items, setting values, and more.
- Use the “Toolbar” on the right side of your screen to change the mind map layout, and shape, add/remove completion markers, add color, insert images, hyperlink text, and add icons for a visually appealing mind map.
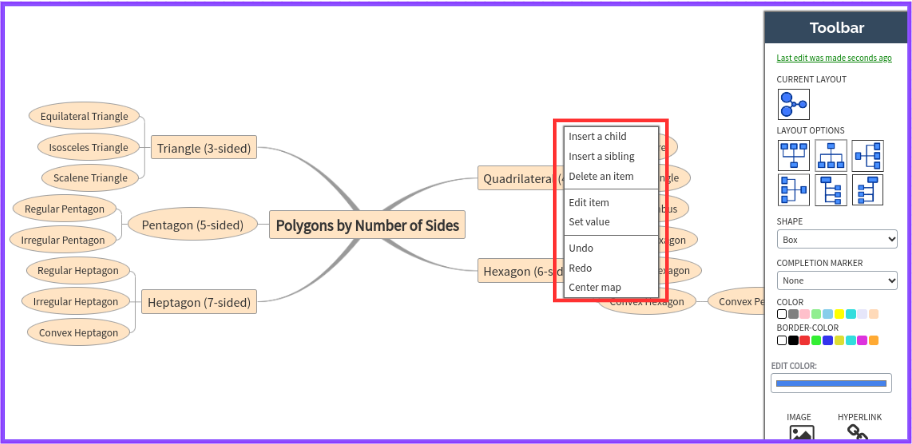
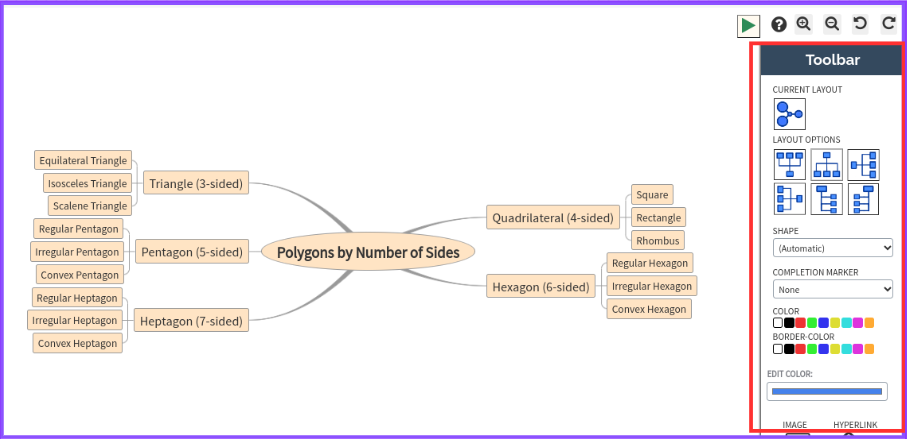
Encourage Students to Try AI-Powered Mind Maps
Once you have created your AI-generated mind map, share it with your students to view/edit the mind map and encourage them to create new mind maps on their own. You can do that as a classroom activity or give it to them as a homework assignment.
How to Share Your Mind Maps
Step 1: Click on the “Share” icon under your created mind map present on the “My Mind Maps” screen.

Step 2: Select the Student(s) list from the available options, then select the student(s) you want to share your mind map with and give them “View” or “Edit” permission access.
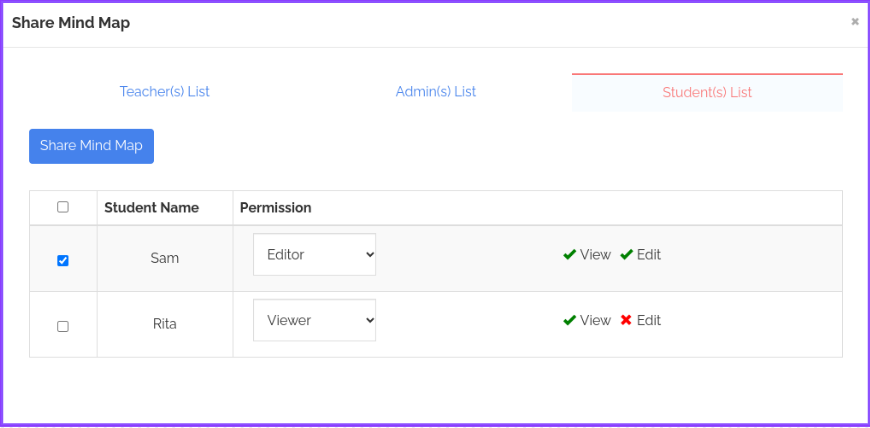
Step 3: The selected student(s) will then be able to view/edit the mind map based on the given permissions from their student accounts under the “Shared Mind Maps” section.
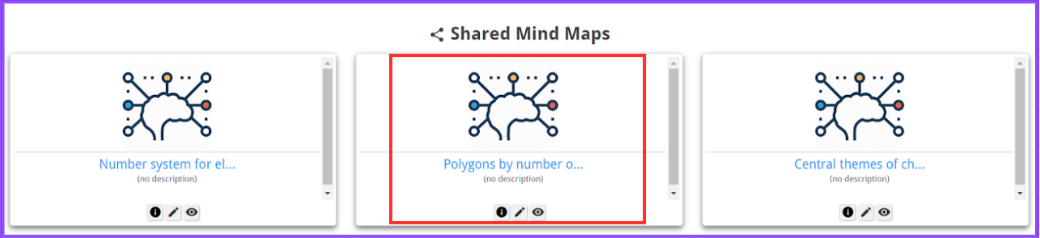
Incorporating Mind Maps into Your Math Classroom
Now that you’ve created your mind map on “Polygons by Number of Sides”, it’s time to integrate it into your math classroom. Here are some suggestions for how to incorporate mind maps effectively:
- Introduction: Begin your lesson by introducing the concept of polygons and their properties using the mind map as a visual aid.
- Exploration: Allow students to explore the mind map independently or in small groups, encouraging them to interact with the information and make connections between different types of polygons.
- Discussion: Facilitate a class discussion based on the mind map, encouraging students to share their observations, ask questions, and engage in critical thinking about the properties of polygons.
- Application: Provide opportunities for students to apply their understanding of polygons by solving problems or completing activities related to polygon properties.
- Assessment: Use the mind map as a formative assessment tool to gauge students’ understanding of polygon properties, either through verbal explanations or written responses.
Conclusion
Mind maps are invaluable tools for enhancing math classroom learning and retention. By leveraging the visual and organizational benefits of mind maps, educators can create engaging learning experiences that inspire curiosity, foster critical thinking, and deepen students’ understanding of mathematical concepts. So why wait? Start incorporating mind maps into your math classroom today and watch as your students’ comprehension and retention soar to new heights.
