Lumos Video Store
This page provides a list of educational videos related to Corresponding Parts. You can also use this page to find sample questions, apps, worksheets, lessons , infographics and presentations related to Corresponding Parts.
Using Corresponding Parts Of Congruent Triangles Are Congruent

By MrPilarski
YouTube presents Using Corresponding Parts Of Congruent Triangles Are Congruent, an educational video resource on math.
Permutations | MathHelp.com

By MathHelp.com
This lesson covers congruent figures. Students learn that if two figures are congruent, then their corresponding parts are congruent. For example, if two triangles are congruent, then their corresponding angles are congruent, and their corresponding sides are congruent. Students are then asked to complete congruence statements using given figures.
Congruent Figures | MathHelp.com

By MathHelp.com
This lesson covers dividing integers. Students learn to divide integers using the following rules. A positive divided by a positive equals a positive. For example, +20 divided by +2 = +10. A positive divided by a negative equals a negative. For example, +20 divided by -2 = -10. A negative divided by a positive equals a negative. For example, -20 divided by +2 = -10. And a negative divided by a negative equals a positive. For example, -20 divided by -2 = +10. In other words, if the signs are the same, the quotient is positive, and if the signs are different, the quotient is negative. Note that any integer divided by zero is undefined. For example, +4 divided by 0 = undefined. And zero divided by any integer (other than zero) is zero. For example, 0 divided by +4 = 0.
The People of Broadcast Journalism

By
Hello. Welcome to this video on the people of broadcast journalism. In the previous video, we talked about new vocabulary we use when talking about the news for television, internet, and radio. In this video, we're going to take a deeper look into the people that deliver the news in video or audio form. We'll talk about news anchors, correspondents, producers, and control room operators.
04 - What is the Unit Circle? Angle Measure in Degrees, Reference Angles & More.
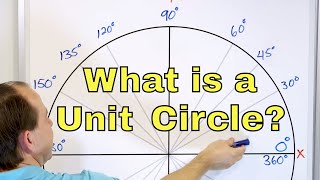
By Math and Science
Quality Math And Science Videos that feature step-by-step example problems!
Work Word Problems | MathHelp.com

By MathHelp.com
To solve a polynomial inequality, like the one shown here, our first step is to write the corresponding equation. In other words, we simply change the inequality sign to an equals sign, and we have x^2 – 3 = 9 – x. Next, we solve the equation. Since we have a squared term, we first set the equation equal to 0. So we move the 9 – x to the left side by subtracting 9 and adding x to both sides of the equation. This gives us x^2 + x – 12 = 0. Next, we factor the left side as the product of two binomials. Since the factors of negative 12 that add to positive 1 are positive 4 and negative 3, we have x + 4 times x – 3 = 0. So either x + 4 = 0 or x – 3 = 0, and solving each equation from here, we have x = -4, and x = 3. Now, it’s important to understand that the solutions to the equation, -4 and 3, represent what are called the “critical values” of the inequality, and we plot these critical values on a number line. However, notice that our original inequality uses a greater than sign, rather than greater than or equal to sign, so we use open dots on our critical values of -4 and positive 3. Remember that ‘greater than’ or ‘less than’ means open dot, and ‘greater than or equal to’ or ‘less than or equal to’ means closed dot. Now, we can see that our critical values have divided the number line into three separate intervals: less than -4, between -4 and 3, and greater than 3. And here’s the important part. Our next step is to test a value from each of the intervals by plugging the value back into the original inequality to see if it gives us a true statement. So let’s first test a value from the “less than -4” interval, such as -5. If we plug a -5 back in for both x’s in the original inequality, we have -5 squared – 3 greater than 9 minus a -5, which simplifies to 25 – 3 greater than 9 + 5, or 22 greater than 14. Since 22 greater than 14 is a true statement, this means that all values in the interval we’re testing are solutions to inequality, so we shade the interval. Next, we test a value from the “between -4 and 3” interval, such as 0. If we plug a 0 back in for both x’s in the original inequality, we have 0 squared – 3 greater than 9 – 0, which simplifies to 0 – 3 greater than 9, or -3 greater than 9. Since -3 greater than 9 is a false statement, this means that all values in the interval we’re testing are not solutions to inequality, so we don’t shade the interval. Next, we test a value from the “greater than 3” interval, such as 4. If we plug a 4 back in for both x’s in the original inequality, we have 4 squared – 3 greater than 9 – 4, which simplifies to 16 – 3 greater than 5, or 13 greater than 5. Since 13 greater than 5 is a true statement, this means that all values in the interval we’re testing are solutions to inequality, so we shade the interval. Finally, we write the answer that’s shown on our graph in set notation. The set of all x’s such that x is less than -4 or x is greater than 3.
16 - What do Imaginary & Complex Roots of Equations Mean?
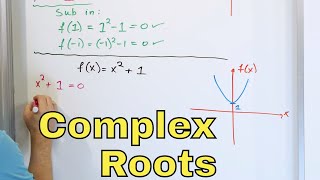
By Math and Science
Quality Math And Science Videos that feature step-by-step example problems!
How To Solve Doppler Effect Physics Problems
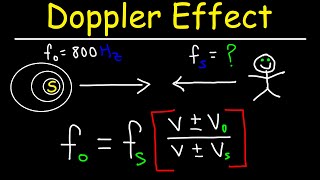
By The Organic Chemistry Tutor
This physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the doppler effect of moving sound waves. it explains how to solve doppler effect problems in physics. Any time the source moves toward the observer or if the observer moves toward the source, the detected frequency will increase - that is - the observed frequency will be greater than the frequency emitted by the source. The source can be an ambulance truck or a police siren. If the source moves away from the observer or if the observer moves away from the source, the detected frequency will decrease. This video contains plenty of examples and practice problems of calculated the frequency detected by the observer.
How to Identify Molecules - Proton NMR: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #26

By Math and Science
Quality Math And Science Videos that feature step-by-step example problems!
Arithmetic Sequences and Arithmetic Series - Basic Introduction

By The Organic Chemistry Tutor
This video provides a basic introduction into arithmetic sequences and series. It explains how to find the nth term of a sequence as well as how to find the sum of an arithmetic sequence. It also discusses how to distinguish a finite sequence from an infinite series. It also includes a few word problems.
Computational Linguistics: Crash Course Linguistics #15

By Math and Science
Quality Math And Science Videos that feature step-by-step example problems!
ALL OF GRADE 9 MATH IN 60 MINUTES!!! (exam review part 3)

By Lumos Learning
Here is a great exam review video reviewing all of the main concepts you would have learned in the MPM1D grade 9 academic math course. The video is divided in to 3 parts. This is part 3: Geometry. In this video you will review parallel line theorems, pythagorean theorem, and volume/surface area of three dimensional shapes.
16 - Domain and Range of a Quadratic Function - Part 1 (Graphing Quadratics)

By Math and Science
Quality Math And Science Videos that feature step-by-step example problems!






