Lumos Video Store
This page provides a list of educational videos related to Multiply Zeros. You can also use this page to find sample questions, apps, worksheets, lessons , infographics and presentations related to Multiply Zeros.
Zero and identity matrices

By Khan Academy
Just as any number multiplied by zero is zero, there is a zero matrix such that any matrix multiplied by it results in that zero matrix. Learn more from Sal.
A Walkthrough of Solving a Quadratic Equation

By Tim Fahlberg
This video gives you a quick walkthrough of how to solve a quadratic equation by factoring. Watch how the Zero Product Property comes into play. Remember, if two numbers multiply to equal zero, at least one of the two MUST be zero. It's an important property of our number system, and it is what allows us to solve by factoring.
[5.NBT.2-1.0] Multiplying/Dividing by 10 - Common Core Standard - Practice Problem
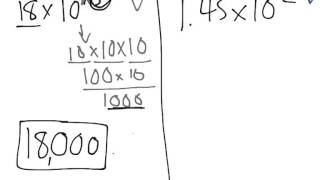
By Front Row
Explain patterns in the number of zeros of the product when multiplying a number by powers of 10, use whole-number exponents to denote powers of 10
Understanding moving the decimal

By Khan Academy
You will notice in this word problem that moving the decimal to the right the same number of times as the number of zeros you multiplying by gets you the answer you desire. Check this out!
Multiplying decimals 3

By Khan Academy
Sometimes multiplying really small decimals (with all those zeros!) can be a little intimidating. Watch as we show you a handy trick to simplify these problems and solve them.
More involved multiplying decimals example

By Khan Academy
Sometimes multiplying really small decimals (with all those zeros!) can be a little intimidating. Watch as we show you a handy trick to simplify these problems and solve them.
Multiplying decimals 2

By Khan Academy
Sometimes multiplying really small decimals (with all those zeros!) can be a little intimidating. Watch as we show you a handy trick to simplify these problems and solve them.
Estimating Products | MathHelp.com

By MathHelp.com
This lesson covers perimeter. Students learn that the perimeter of a figure is the distance around the figure, so the perimeter of a figure can be found by adding the lengths of its sides. Since all four sides of a square are equal in length, the perimeter of a square that has a side with a length of 8 feet is 8 + 8 + 8 + 8, or 32 feet. Since opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length, the perimeter of a rectangle that is 4.5 meters by 6.2 meters is 4.5 + 4.5 + 6.2 + 6.2, or 21.4 meters.
8th Grade Math | MathHelp.com

By MathHelp.com
This lesson covers estimating products. Students learn to estimate a product or quotient by first rounding each number to one non-zero digit. For example, to estimate 8,291 x 27, first round 8,291 down to 8,000, and round 27 up to 30, then multiply 8,000 x 30 to get 240,000.
Imaginary Numbers | MathHelp.com

By MathHelp.com
This lesson covers estimating quotients. Students learn to estimate a product or quotient by first rounding each number to one non-zero digit. For example, to estimate 8,291 x 27, first round 8,291 down to 8,000, and round 27 up to 30, then multiply 8,000 x 30 to get 240,000.
Multiplying and Dividing by Powers of 10

By jimbabweiberg
The instructor uses an interactive white board to show that multiplying a decimal by 10 100 1 000 or 10 000 moves the decimal one two three or four places to the right. He displays a calculator to show this as well. He also explains and shows that dividing by a power of 10 moves the decimal place to the left according to the number of zeros in the number you are multiplying by.
Rational Exponents | MathHelp.com

By MathHelp.com
In this example, we’re asked to write “a” to the negative 3rd squared in simplest form without negative or zero exponents. Remember that the power rule tells us that when we have a power taken to another power, such as a to the negative 3rd squared, we multiply the exponents. So we have a to the -3 times 2, or a to the negative 6th. Finally, remember from our study of negative exponents that a to the negative 6th can be written as 1 over a to the positive 6th. So a to the negative 3rd squared simplifies to 1 over a to the 6th.
Units of Measurement | MathHelp.com

By MathHelp.com
This lesson covers vertical angles. Students learn the definition of vertical angles and the vertical angle theorem, and are asked to find the measures of vertical angles using Algebra. Students also solve two-column proofs involving vertical angles.
Negative Exponents | MathHelp.com

By MathHelp.com
In this example, we’re given the functions f(x) = 3x – 2 (read as “f of x equals…”) and g(x) = root x, and we’re asked to find the composite functions f(g(9)) (read as “f of g of 9”) and g(f(9). To find f(g(9)), we first find g(9). Since g(x) = root x, we can find g(9) by substituting a 9 in for the x in the function, to get g(9) = root 9, and the square root of 9 is 3, so g(9) = 3. Now, since g(9) = 3, f(g(9)) is the same thing as f(3), so our next step is to find f(3). And remember that f(x) = 3x – 2, so to find f(3), we substitute a 3 in for the x in the function, and we have f(3) = 3 times 3 minus 2. Notice that I always use parentheses when substituting a value into a function, in this case 3. Finally, 3 times 3 minus 2 simplifies to 9 minus 2, or 7, so f(3) = 7. Therefore, f(g(9)) = 7. Next, to find g(f(9), we first find f(9). Since f(x) = 3x - 2, we find f(9) by substituting a 9 in for the x in the function, to get f(9) = 3 times 9 minus 2, which simplifies to 27 – 2, or 25, so f(9) = 25. Now, since f(9) = 25, g(f(9)) is the same thing as g(25), so our next step is to find g(25). And remember that g(x) = root x, so to find g(25), we substitute a 25 in for the x in the function, to get g(25) = root 25. Finally, the square root of 25 is 5, so g(25) = 5. Therefore, g(f(9)) = 5. It’s important to recognize that





