Lumos Video Store
This page provides a list of educational videos related to Finding the Slope of a Line. You can also use this page to find sample questions, apps, worksheets, lessons , infographics and presentations related to Finding the Slope of a Line.
Find the Equation of a Line Using Point-Slope Form
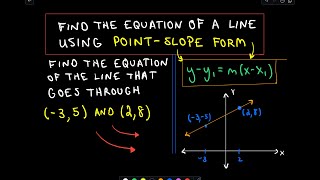
By PatrickJMT
Find the Equation of a Line Using Point-Slope Form - I show one complete example of finding the equation of a line using point-slope form. For more free math videos, visit http://PatrickJMT.com
Equation of the normal line at a point

By TheIntegralCALC
http://integralcalc.com/ Learn how to find the equation of the normal line at a given point. To find the equation of the normal line, you'll need to first calculate the derivative of the function, then plug the given point into the derivative to find the slope of the tangent line. Plug the slope and the given point into the point-slope formula for the equation of the line to find the equation of the tangent line. Then take the negative reciprocal of the slope of the tangent line to find the slope of the normal line, which is the line perpendicular to the tangent line. Finally, plug the new slope and the given point into the point-slope formula for the equation of the line to find the equation of the normal line
Finding the slope of a line from its graph | Algebra I

By Khan Academy
This video lecture series on Worked Examples in Algebra from Khan Academy includes Solving Equations, Solving Word Problems, Solving for a variable, Absolute Value and Number Lines, Patterns in Sequences, Functional Relationships, Domain and Range, Rate Problems, Linear Functions, Slope of a Line, X and Y intercepts, Equation of a Line, Parallel Lines, Perpendicular Lines, Solving Inequalities and more...
Slope-intercept equation from two solutions example | Algebra I | Khan Academy

By Khan Academy
Find the equation of a line given two points, neither of which is the y-intercept. To do this, first find the slope, then you may either graph the line (as is done here), or plug in one of the points in for "x" and "y" into y = mx + b to solve for "b."
Inverse Functions | MathHelp.com

By MathHelp.com
In this example, we’re given a relation in the form of a chart, and we’re asked to find the inverse of the relation, then graph the relation and its inverse. To find the inverse of a relation, we simply switch the x and y values in each point. In other words, the point (1, -4) becomes (-4, 1), the point (2, 0) becomes (0, 2), the point (3, 1) becomes (1, 3), and the point (6, -1) becomes (-1, 6). Next, we’re asked to graph the relation and its inverse, so let’s first graph the relation. Notice that the relation contains the points (1, -4,), (2, 0), (3, 1), and (6, -1). And the inverse of the relation contains the points (-4, 1), (0, 2), (1, 3), and (-1, 6). Finally, it’s important to understand the following relationship between the graph of a relation and its inverse. If we draw a diagonal line through the coordinate system, which is the line that has the equation y = x, notice that the relation and its inverse are mirror images of each other in this line. In other words, the inverse of a relation is the reflection of the original relation in the line y = x.
Velocity Time Graphs, Acceleration & Position Time Graphs - Physics

By The Organic Chemistry Tutor
This physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into motion graphs such as position time graphs, velocity time graphs, and acceleration time graphs. It explains how to use area and slope to calculate the velocity, acceleration, displacement, and whether if the particle is speeding up or slowing down. It also explains how to determine if the velocity is increasing or if the acceleration is positive.
Systems of Three Equations | MathHelp.com

By MathHelp.com
Here we’re asked to graph the following function and use the horizontal line test to determine if it has an inverse. And if so, find the inverse function and graph it. So let’s start by graphing the given function, f(x) = 2x – 4, and remember that f(x) is the same as y, so we can rewrite the function as y = 2x – 4. Now, we simply graph the line y = 2x – 4, which has a y-intercept of -4, and a slope of 2, or 2/1, so we go up 2 and over 1, plot a second point and graph our line, which we’ll call f(x). Next, we’re asked to use the horizontal line test to determine if the function has an inverse. Since there’s no way to draw a horizontal line that intersects more than one point on the function, the function does have an inverse. So we need to find the inverse and graph it. To find the inverse, we switch the x and the y in original function, y = 2x – 4, to get x = 2y – 4. Next, we solve for y, so we add 4 to both sides to get x + 4 = 2y, and divide both sides by 2 to get 1/2x + 2 = y. Next, let’s flip our equation so that y is on the left side, and we have y = 1/2x + 2. Finally, we replace y with the notation that we use for the inverse function of f, as shown here. And remember that we’re asked to graph the inverse as well, so we graph y = ½ x + 2. Our y-intercept is positive 2, and our slope is ½, so we go up one and over 2, plot a second point, graph the line, and label it as the inverse function of f. Notice that the graph of the inverse function is a reflection of the original function in the line y = x.
ALL OF GRADE 9 MATH IN 60 MINUTES!!! (exam review part 2)

By Lumos Learning
Here is a great exam review video reviewing all of the main concepts you would have learned in the MPM1D grade 9 academic math course. The video is divided in to 3 parts. This is part 2: Linear Relations. In this video you will review everything there is to know about y=mx+b, scatterplots, and distance time graphs.
01 - Direct Variation and Proportion in Algebra - Part 1 (Constant of Variation & More)

By Math and Science
Quality Math And Science Videos that feature step-by-step example problems!
8th Grade Math

By Lumos Learning
8th grade math lesson addressing Common Core Standards (Massachusetts Curriculum Framework Standard 8.EE.6).









