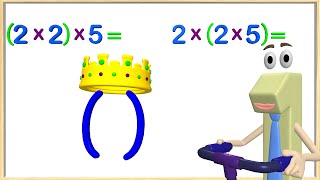[3.OA.5-1.0] Multiplication Properties - Common Core Standard - By Front Row
| 00:0 |
DESCRIPTION:
Discover more Common Core Math at https://www.frontrowed.comApply properties of operations as strategies to multiply.2 Examples: If 6 ÃÆââ¬â 4 = 24 is known, then 4 ÃÆââ¬â 6 = 24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 ÃÆââ¬â 5 ÃÆââ¬â 2 can be found by 3 ÃÆââ¬â 5 = 15, then 15 ÃÆââ¬â 2 = 30, or by 5 ÃÆââ¬â 2 = 10, then 3 ÃÆââ¬â 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8 ÃÆââ¬â 5 = 40 and 8 ÃÆââ¬â 2 = 16, one can find 8 ÃÆââ¬â 7 as 8 ÃÆââ¬â (5 2) = (8 ÃÆââ¬â 5) (8 ÃÆââ¬â 2) = 40 16 = 56. (Distributive property.)Front Row is a free, adaptive, Common Core aligned math program for teachers and students in kindergarten through eighth grade. Front Row allows students to practice math at their own pace - learning advanced concepts when they 're ready and receiving remediation when they struggle. Front Row provides teachers with access to a detailed data dashboard and weekly email reports that show which standards are causing students difficulty, what small groups can be formed for interventions, and how their students are progressing in math.Discover more Common Core Math at https://www.frontrowed.com
OVERVIEW:
[3.OA.5-1.0] Multiplication Properties - Common Core Standard is a free educational video by Front Row.It helps students in grades 3 practice the following standards 3.OA.B.5.
This page not only allows students and teachers view [3.OA.5-1.0] Multiplication Properties - Common Core Standard but also find engaging Sample Questions, Apps, Pins, Worksheets, Books related to the following topics.
1. 3.OA.B.5 : Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. Examples: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15 then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10 then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.) (Students need not use formal terms for these properties.).





![[3.NF.3b-1.0] Equivalent Fractions - Common Core Standard](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/gJaBKt1Qhm8/mqdefault.jpg)